Redirects in WordPress are a powerful tool for managing URLs, improving navigation, and enhancing SEO. However, incorrect or unnecessary redirects can cause issues like redirect loops, broken links, or loss of traffic. If you’ve encountered such problems, this guide will help you identify, remove, and troubleshoot redirects in WordPress.
Understanding Redirects in WordPress
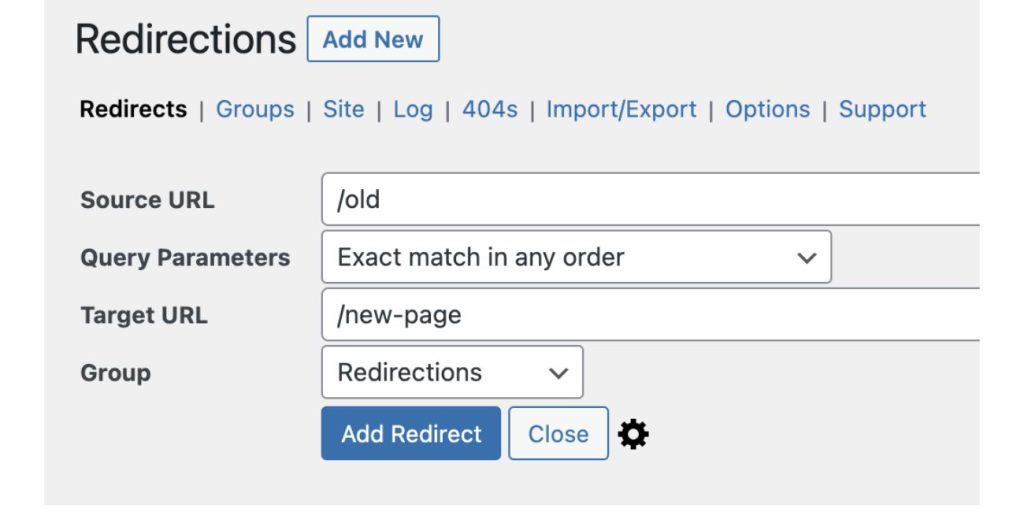
Redirects are instructions that send users from one URL to another. They are often used for site migrations, fixing broken links, or managing outdated content.
Types of Redirects
- 301 Redirects: Permanent redirects that tell search engines the original URL has moved permanently.
- 302 Redirects: Temporary redirects, used when a URL change is not permanent.
- 307 Redirects: Temporary redirects similar to 302, but maintaining the original request method.
Redirects are essential, but misconfigured rules can disrupt your site, necessitating their removal.
How Identify Active Redirects on Your WordPress Site
Before you can undo a redirect, you need to locate the source.
1. Use Plugins to Check Redirects
- Redirection Plugin: Navigate to Tools > Redirection in your WordPress dashboard to view all redirect rules.
- Yoast SEO or Rank Math: These SEO plugins include features to manage and monitor redirects.
2. Inspect .htaccess File
The .htaccess file in your WordPress root directory often contains redirect rules, especially for Apache servers. Use an FTP client or file manager to check for rules like:
Redirect 301 /old-url /new-url
3. Use Hosting Control Panel
Some hosting providers manage redirects directly. Log in to your hosting control panel (e.g., cPanel or Plesk) and check the redirect manager for active rules.
Steps to Undo Redirects in WordPress
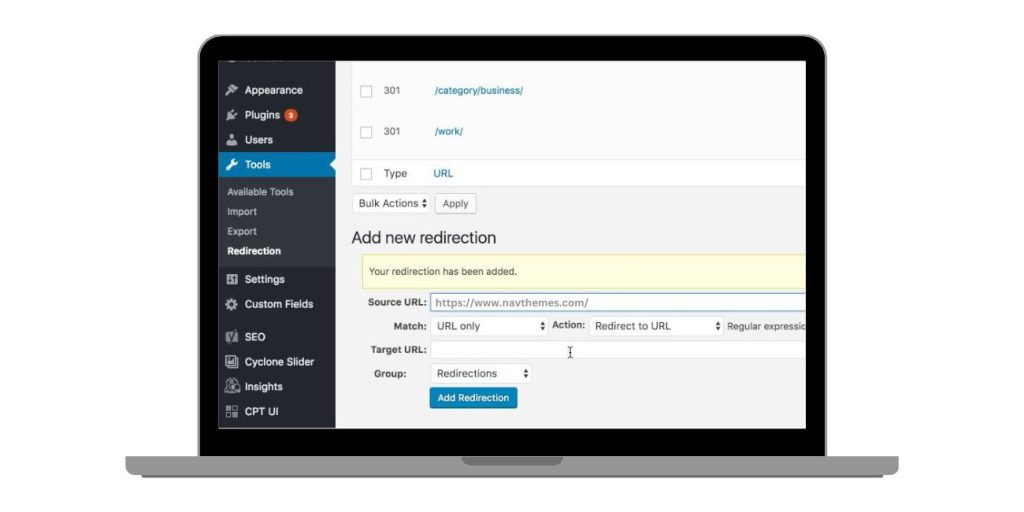
Once you’ve identified the source, follow these steps to remove unwanted redirects.
1. Undo Redirects via Plugins
If a plugin like Redirection is managing the redirect:
- Go to Tools > Redirection in your dashboard.
- Locate the redirect rule you want to remove.
- Click Delete or Disable to stop the redirection.
2. Remove Redirect Rules from .htaccess
- Access your site’s .htaccess file using an FTP client or file manager.
- Look for lines starting with
RedirectorRewriteRule. - Delete or comment out the lines responsible for the redirect.
- Save the file and test your site to ensure the rule is removed.
3. Undo Hosting-Managed Redirects
- Log in to your hosting control panel.
- Navigate to the Redirects section.
- Locate and delete the redirect rules you no longer need.
4. Clear Browser Cache and Test
Redirects can sometimes persist due to cached data. Clear your browser cache or test in incognito mode to confirm the changes.
Troubleshooting Redirect Issues
If problems persist after removing redirects, here are some common issues and fixes:
Fixing Redirect Loops
- Check your WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL) in Settings > General. They should match your intended domain.
- Ensure no conflicting rules exist in your .htaccess file or plugins.
Ensuring Redirects Are Fully Removed
- Use tools like Redirect Checker or HTTP Header Inspector to confirm that the redirect is no longer active.
- Test the affected URLs to verify they resolve correctly.
Resolving Plugin Conflicts
- Deactivate all plugins and reactivate them one by one to identify conflicts.
- Update plugins to their latest versions for compatibility.
Resetting Permalinks
- Go to Settings > Permalinks in your WordPress dashboard.
- Click Save Changes without making modifications.
- This action refreshes the permalink structure and resolves minor redirect issues.
Best Practices for Managing Redirects
To avoid future issues, follow these best practices:
1. Use Redirects Judiciously
Only implement redirects when necessary, such as fixing broken links or managing page migrations.
2. Regularly Audit Redirects
Use tools like the Redirection plugin or Google Search Console to monitor and review redirect rules periodically.
3. Backup Before Making Changes
Always create a backup of your WordPress site before modifying redirect rules or the .htaccess file. Use a backup plugin or hosting service to ensure you can restore your site if needed.
4. Document Your Redirect Changes
Maintain a log of redirect additions, modifications, and removals for future reference. This is especially helpful for large sites with complex redirect structures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs )
How Do I Find Out What Redirects Are Active on My Site?
Use plugins like Redirection or inspect your .htaccess file. Hosting control panels may also list active redirects.
Can Removing Redirects Impact SEO?
Yes, especially if you remove 301 redirects linked to indexed URLs. Use tools like Google Search Console to ensure removed redirects don’t cause broken links.
What Should I Do If I Accidentally Delete a Critical Redirect?
Restore the redirect using your backup or re-create the rule in your plugin or .htaccess file.
Conclusion
Redirects are a vital part of WordPress site management, but they can cause problems when misconfigured. By following this guide, you can identify, remove, and troubleshoot redirects effectively, ensuring your site runs smoothly and remains user-friendly.
Have questions or tips about managing redirects in WordPress? Share them in the comments below, and don’t forget to share this guide with others!

